Have you ever been visited Africa? Africa is a great land for many animals, especially in African Savanna. The African savanna ecosystem is a tropical grassland with warm temperatures year-round and with its highest seasonal rainfall in the summer. The savanna is characterized by grasses and small or dispersed trees that do not form a closed canopy, allowing sunlight to reach the ground. The African savanna contains a diverse community of organisms that interact to form a complex food web.
A community is a group of organisms interacting in a specific region under similar environmental conditions. A food chain is a group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, prey to predators, and scavengers to decomposers. The arrows in a food chain represent the flow of energy and matter between feeding (trophic) levels. Food chains show only one path of food and energy through an ecosystem. In most ecosystems, organisms can get food and energy from more than one source, and may have more than one predator.
Healthy, well-balanced ecosystems are made up of multiple, interacting food chains, called food webs. Carnivores (lions, hyenas, leopards) feed on herbivores (impalas, warthogs, cattle) that consume producers (grasses, plant matter). Scavengers (hyenas, vultures) and decomposers/detritivores (bacteria, fungi, termites) break down organic matter, making it available to producers and completing the food cycle (web). Humans are part of the savanna community and often compete with other organisms for food and space.
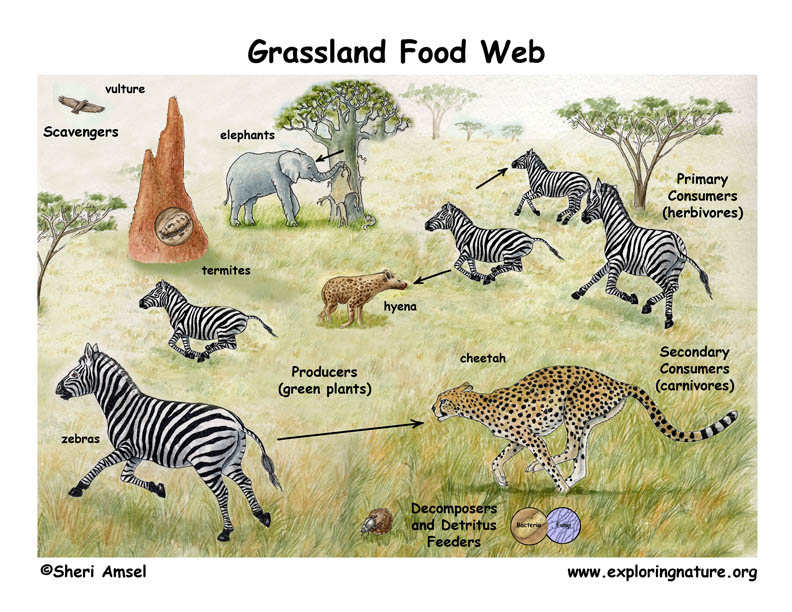
- Producer: organism on the food chain that can produce its own energy and nutrients. Examples: grasses, Jackalberry tree, Acacia tree
- Primary consumer/herbivore: organism that eats mainly plants. Examples: cows, impalas, warthogs, zebras
- Secondary consumer/carnivore: organism that eats meat. Examples: leopard, lion
- Omnivore: organism that eats a variety of organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. Examples: humans, aardvarks
- Decomposer/detritivores: organisms that break down dead plant and animal material and waste and release it as energy and nutrients in the ecosystem. Examples: bacteria, fungi, termites
- Scavenger: animal that eats dead or rotting animal flesh. Examples: vultures, hyenas
- Insectivore: organism that mostly eats insects. Example: Red-billed oxpecker


0 comments:
Post a Comment